Introduction to Music Cadences:
What is a cadence? Music Cadences are useful not only to understand better what you play, but also it will help you improvise in any music key.
Cadences - Music Definition
When we teach music theory in Cork Music School, we always say that a cadence is the harmonic link/s at the end of a musical phrase/section/piece. It is a harmonic function, thus, related to chords and it is related to a sort of sensation of ending or pause in music. If you want to have proper music education you must know that there two kinds of Cadences. One sounds conclusive and the other one sounds suspensive.
1- Authentique Cadence (Conclusive)
Authentique cadences are cadences that describe a full tonal confirmation, in which the tonic chord generally coincides with the first beat of the measure. There are two types of Authentique Cadences: Perfect and Imperfect
1.1- Perfect Authentique Cadences
Two chords, one is a Dominant Chord (V), sometimes(not necessary) it includes a 7th. The other one is a Tonic Chord. Both chords must have the root note on the bass.

1.2- Imperfect Authentique Cadences
It works same way as perfect. In this case, one of the two chords are inverted, meaning that one of the two chords do not have the root note on the bass.
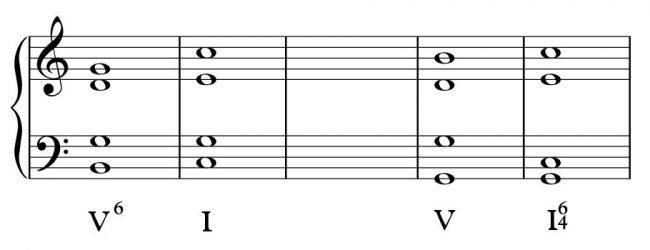
2- Plagal Cadence (Conclusive)
Tow chords: One is a subdominant chord (IV), the other one is a tonic chord (I). Both in root position. The subdominant chord may also be exchanged by a II or VI degrees.
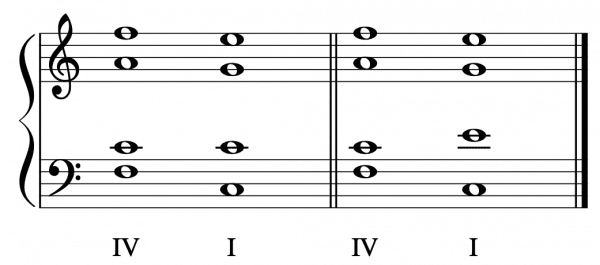
NOTE: Plagal cadences may also imperfect if one of the two chords are inverted.
3- Half Cadence (Suspensive)
This cadence is produced with the momentaneous repose of another degree different from the Tonic (I). The most common degrees for this moment of repose are the Dominant and Subdominant, althought they may also be produced on the II, VI, III degrees.
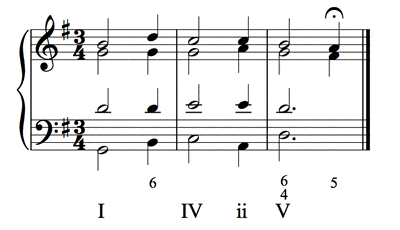
Important Note: As you can see in the previous example, cadences may be preceded by other chords/degrees.
4- Deceptive Cadence (Suspensive)
A deceptive cadence is a progression in which the dominant chord (V) resolves to a chord other than the tonic (I). Most of the times, the dominant chord (V) will lead to the submediant chord (vi in major keys, VI in minor keys). The name “deceptive” expresses that the resolution seems to resolve in a tonic chord. Instead it leads into a different chord/degree.
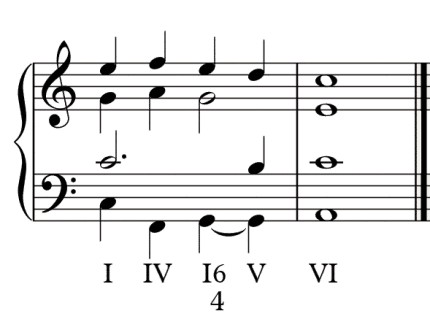
Practicing and getting used to the sound of music cadences
Even if you are not a pianist, Bach Chorals will help you master the art of music cadences.
5- Importance of Music Cadences:
Establishing Structure: Cadences define the structure of a musical piece by signaling the end of a musical phrase or section. They help organize the music into coherent units, enhancing its flow and coherence.
Creating Emotion: Different types of cadences evoke distinct emotions. For instance, the authentic cadence, with its stable and final sound, brings a sense of completion and satisfaction, while the plagal cadence provides a more gentle and contemplative feeling.
Building Tension and Release: Cadences can introduce tension and release in music. Suspended cadences, for instance, create a feeling of anticipation before resolving to a stable chord, adding depth and drama to the composition.
6- Utilizing Music Cadences:
Enhancing Song Endings: Cadences are frequently employed to conclude songs or sections, leaving a lasting impression on the listener. Experiment with various cadence types to find the most fitting one for your musical expression.
Emphasizing Musical Phrases: Implementing cadences at the end of musical phrases can highlight important moments and ensure the music flows smoothly from one phrase to another.
Balancing Emotional Intensity: Varying the cadences used throughout a piece can help control the emotional intensity. Reserve stronger cadences, like the authentic cadence, for significant moments and use weaker ones, such as half cadences, to create a sense of continuation.
Modulations and Transitions: Cadences are indispensable tools for modulating between keys or transitioning to different sections. A cadence in the new key can smoothly guide listeners to the new tonal center.
7- Conclusion
In summary, cadences are vital components of music that bring structure, emotion, and tension to compositions. Mastering the art of utilizing cadences allows musicians and composers to manipulate the flow and impact of their music, captivating audiences and leaving a lasting impression. By experimenting with various cadences and understanding their effects, musicians can enhance their musical storytelling and create captivating, memorable pieces.










